卵巢癌,美国在研的206项基金简述(2024)
2024-10-25 Hanson临床科研 Hanson临床科研 发表于上海
我们仅对美国国立卫生研究院(NIH)资助的在研卵巢癌相关项目进行梳理,希望给同仁们的选题思路提供一点启发。
卵巢癌(Ovarian Cancer),是一种起源于卵巢的恶性肿瘤,由于其在早期阶段常无明显症状,通常在晚期被发现,这大大降低了治疗的成功率。
尽管近年来在卵巢癌的诊断和治疗方面取得了显著进展,但仍存在一些重要而未解决的临床问题:
-
早期检测:由于缺乏有效的早期筛查工具,大多数卵巢癌在被诊断时已处于晚期。研究者正在寻找更有效的生物标志物和筛查方法以提高早期诊断率。
-
治疗反应:卵巢癌对化疗的反应具有个体差异,一些患者可能对标准治疗产生耐药。寻找新的药物和治疗策略以覆盖更广泛的患者群体是迫切需要的。
-
复发率高:卵巢癌的复发率较高,尤其是晚期患者。如何管理复发和寻找有效的二线及以上治疗方案是当前的挑战。
-
遗传因素:约10-15%的卵巢癌与遗传因素有关,主要与BRCA1和BRCA2基因突变相关。提供遗传咨询和管理高风险个体的策略需要进一步优化。
总体而言,卵巢癌的研究和临床治疗领域仍面临许多挑战,未来的工作需要集中在提高早期检测率、发展个体化的治疗方案以及管理复发病例上,以提高患者的生存率和生活质量。
我们仅对美国国立卫生研究院(NIH)资助的在研卵巢癌相关项目进行梳理,希望给同仁们的选题思路提供一点启发。
2024年,以“Ovarian Cancer”为检索词、在题目中进行检索,美国NIH针对卵巢癌的在研有206项。
一,谁获得了这些研究?
1,在研卵巢癌基金最多的PI
-
MAGEE-WOMEN'S RES INST AND FOUNDATION 的 BUCKANOVICH, RONALD J
-
UNIVERSITY OF TX MD ANDERSON CAN CTR 的 SOOD, ANIL K
-
MAYO CLINIC ROCHESTER 的 KAUFMANN, SCOTT H
-
MASSACHUSETTS GENERAL HOSPITAL 的 SKATES, STEVEN J
-
UNIVERSITY OF TX MD ANDERSON CAN CTR 的 ZHANG, RUGANG
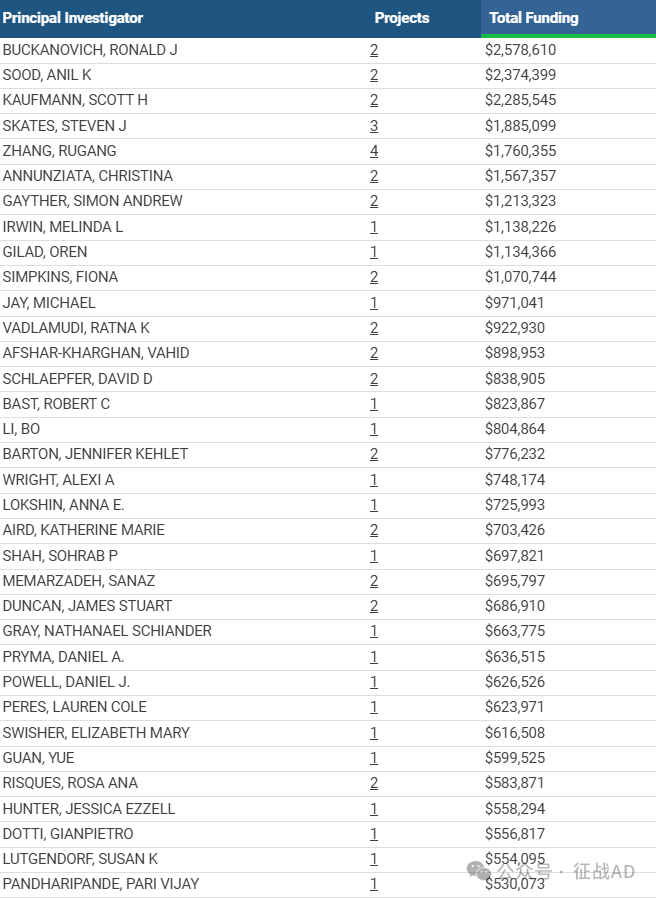
2,卵巢癌基金最多的研究机构
-
德克萨斯大学 MD 安德森癌症中心
-
匹兹堡大学匹兹堡分校
-
约翰霍普金斯大学
-
梅奥诊所罗切斯特
-
丹娜法伯癌症研究所等
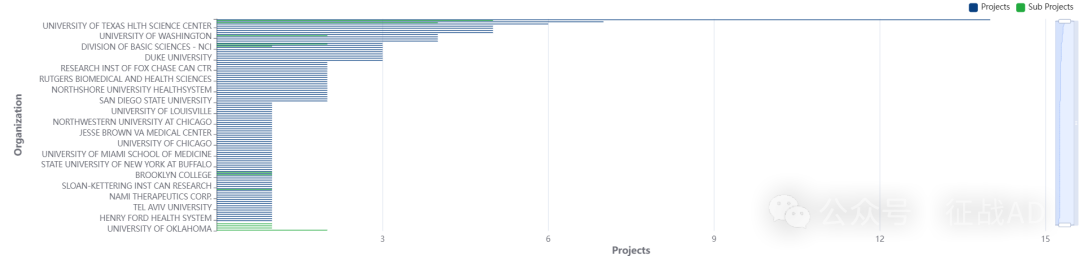
二,卵巢癌研究热点是什么?
卵巢癌研究领域总览(根据关键词)
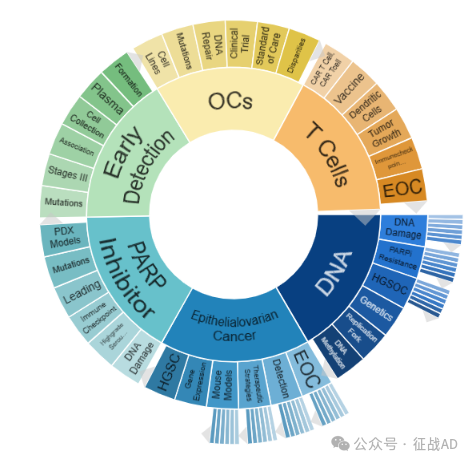
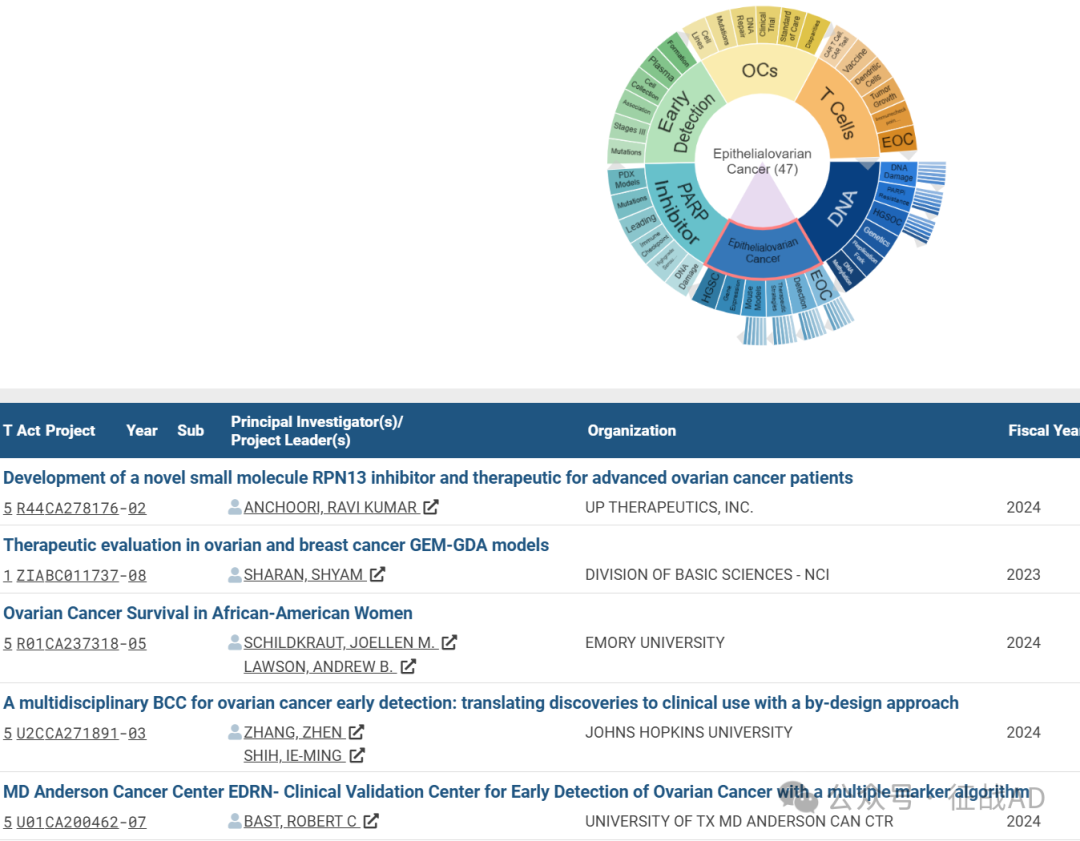
A,关于上皮性卵巢癌(Epithelialovarian Cancer)的研究项目最多
有 47 项在研基金涉及到了上皮性卵巢癌,关注最多的方面包括检测(Detection)、治疗策略(Therapeutic Strategies)、小鼠模型(Mouse Models)、基因表达(Gene Expression)、HGSC、EOC等研究。
B,关于DNA的研究项目
有 45 项在研基金涉及到了DNA,关注最多的方面包括DNA损伤(DNA Damage)、PARP抑制剂耐药性(PARPi Resistance)、高级别浆液性卵巢癌HGSOC、遗传学(Genetics)、复制叉(Replication Fork)、DNA甲基化(DNA Methylation)等研究。

C,关于PARP抑制剂(PARP Inhibitor)的研究项目
有 32 项在研基金涉及到了PARP抑制剂,关注最多的方面包括PDX模型(PDX Models)、突变(Mutations)、导致(Leading)、免疫检查点(Immune Checkpoint)、高级别浆液性卵巢癌(Highgrage Serous Ovariancancer)、DNA损伤(DNA Damage)等研究。
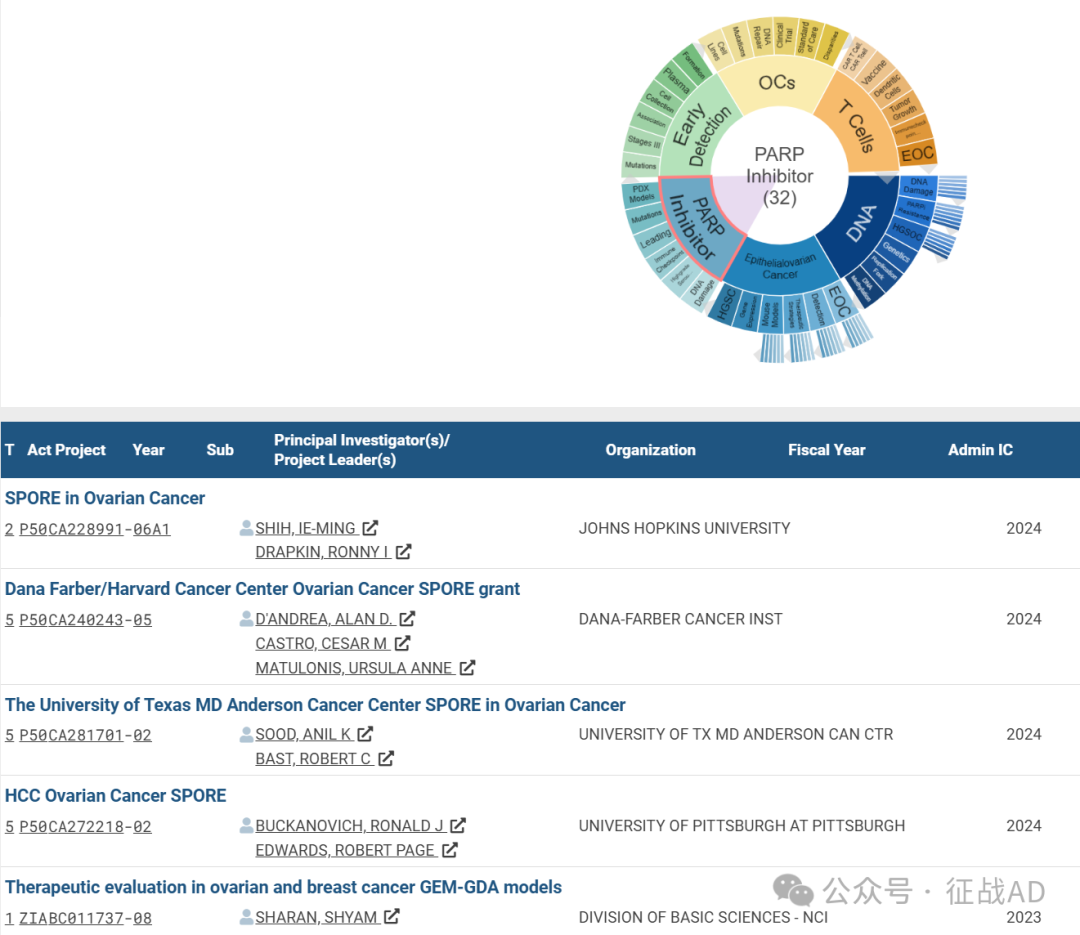
其他卵巢癌研究大的方向也包括早期检测(Early Detection)、T细胞(T Cells)、OCs等。
三,借鉴与突破
我们也分享在卵巢癌领域的几项课题摘要,希望对同仁们有所启发。
A,SPORE in Ovarian Cancer
This Johns Hopkins-University of Pennsylvania Ovarian Cancer SPORE application focuses on reducing ovarian cancer incidence and mortality by translating new laboratory-based discoveries into improvements in ovarian cancer diagnosis and treatment. This highly translational program contains three hypothesis-driven Research Projects, three Core Resources, the Career Enhancement Program (CEP), and the Developmental Research Program (DRP). The objective of Project 1 is to develop a novel brush-based approach to sample fallopian tubes and ovaries for precursor lesions and to define the molecular attributes of detected precursors for proper clinical management. The goal of Project 2 and Project 3 is to provide critical preclinical and early clinical data for developing more effective combined therapy to treat advanced ovarian cancer, especially for recurrent diseases. Specifically, Project 2 will evaluate cyclin E1 protein as a biomarker of ovarian cancers responsive to a new WEE1 inhibitor. Resistance will be addressed with combination WEE1 and ATR inhibition and underlying mechanism of response and resistance will be defined by treatment-related proteins identified at stressed replication forks. Project 3 will exploit a DNA repair vulnerability in ARID1A mutant ovarian cancers. Specifically, the clinical efficacy of the combination of temozolomide and the PARP inhibitor, senaparib, will be evaluated in a Phase II trial. All the three new projects originate from the current CEP/DPR projects. These Projects are supported by an Administrative Core, a Biorepository/Pathology Core, and a Computation/Biostatistics Core.
B, Dana Farber/Harvard Cancer Center Ovarian Cancer SPORE grant
Through this SPORE application, we have tried to address several of the most urgent questions in ovarian cancer therapy.
First, PARP inhibitors are a new and essential feature of high grade serous ovarian cancer (HGSC) therapy, but many patients eventually have cancer progression on these agents. Accordingly, in Project 1, we have designed clinical trials with drug combinations and correlative studies which will allow us to systematically extend the use of PARP inhibitors.
Second, we recognize the emerging impact of immunotherapy on solid tumor treatment. Thus, in Project 2, we have designed a novel vaccine trial for ovarian cancer patients.
Third, HGSC patients with primary refractory disease or those patients with recurrence whose cancer harbor underlying RAS mutations such as low grade serous or mucinous cancers pose a particularly difficult clinical problem. Accordingly, in Project 3, we will explore novel non-platinum drug combinations, such as the combination of a BCL inhibitor and a MEK inhibitor, and will examine predictive biomarkers and tumor responses evident in the extracellular activity.
The Specific Aims of this DF/HCC ovarian cancer SPORE are as follows: Aim 1 (Project 1): ATR inhibitor-mediated reversal of PARP inhibitor resistance in high-grade serous ovarian cancer (HGSOC); Aim 2 (Project 2): Combined personal neoantigen-targeting cancer vaccines with immune checkpoint blockade for ovarian cancer; Aim 3 (Project 3): Evaluation of the Efficacy of Trametinib + Navitoclax in recurrent ovarian carcinoma.
本网站所有内容来源注明为“梅斯医学”或“MedSci原创”的文字、图片和音视频资料,版权均属于梅斯医学所有。非经授权,任何媒体、网站或个人不得转载,授权转载时须注明来源为“梅斯医学”。其它来源的文章系转载文章,或“梅斯号”自媒体发布的文章,仅系出于传递更多信息之目的,本站仅负责审核内容合规,其内容不代表本站立场,本站不负责内容的准确性和版权。如果存在侵权、或不希望被转载的媒体或个人可与我们联系,我们将立即进行删除处理。
在此留言


















#卵巢癌# #美国国立卫生研究院#
40