JCEM:骨骼肌慢肌纤维的比例与胰岛素反应性有关
2013-03-22 desperado-c 丁香园
代谢综合征患者肌肉Ⅰ型纤维中胰岛素受体、IRS-1,GLUT4,ATP合成酶比例下降 代谢综合征是人们发生2型糖尿病的高危因素,是以中心性肥胖伴有血脂异常、高血压和高血糖为特征。为了确定代谢综合征患者胰岛素抵抗与肌肉纤维组成如何相关,来自美国东田纳西州立大学Quillen医学院的Charles A Stuart教授及其团队进行了一项研究,该研究认为代谢综合征患者肌肉Ⅰ型纤维比例的降低与胰岛素
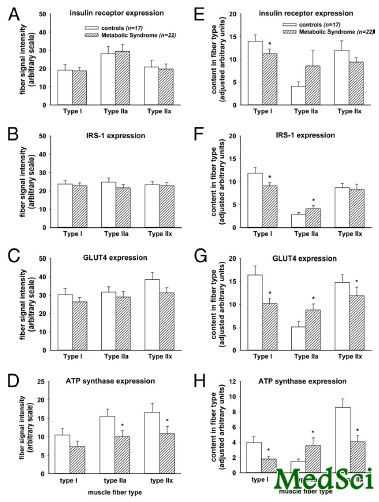
代谢综合征患者肌肉Ⅰ型纤维中胰岛素受体、IRS-1,GLUT4,ATP合成酶比例下降
代谢综合征是人们发生2型糖尿病的高危因素,是以中心性肥胖伴有血脂异常、高血压和高血糖为特征。为了确定代谢综合征患者胰岛素抵抗与肌肉纤维组成如何相关,来自美国东田纳西州立大学Quillen医学院的Charles A Stuart教授及其团队进行了一项研究,该研究认为代谢综合征患者肌肉Ⅰ型纤维比例的降低与胰岛素抵抗的严重性相关。该研究结果在线发表在2013年3月14日美国《临床内分泌代谢杂志》(Journal of clinical endocrinology and metabolism)上。
该研究在39例久坐的男性和女性受试者(包括22例代谢综合征)中采用正常血糖钳夹技术和进行股外侧肌活检量化胰岛素反应性。采用免疫印迹法和免疫组织化学法定量胰岛素受体、胰岛素受体底物-1(IRS-1)、GLUT4和ATP合成酶的表达。
该研究结果表明,代谢综合征受试者有较少的Ⅰ型纤维和更多的混合纤维(Ⅱa型)。胰岛素反应性和最大摄氧量与Ⅰ型纤维比例相关。胰岛素受体、IRS-1和GLUT4在整块肌肉的表达没有区别,当校正肌纤维比例和肌纤维尺寸时,胰岛素受体、IRS-1和GLUT4在代谢综合征患者Ⅰ型纤维的表达显著减少。脂肪氧化和肌肉线粒体表达在代谢综合征患者中没有区别。
该研究发现,代谢综合征患者肌肉Ⅰ型纤维比例的降低与胰岛素抵抗的严重性相关。即使整块肌肉含量正常,胰岛素作用的关键因素在Ⅰ型肌肉纤维始终较少,提示他们的分布在介导胰岛素效应中具有重要作用。
与胰岛素相关的拓展阅读:

Context
The metabolic syndrome, characterized by central obesity with dyslipidemia, hypertension, and hyperglycemia identifies people at high risk for type 2 diabetes.
Objective
Determine how the insulin resistance of the metabolic syndrome is related to muscle fiber composition.
Design
Thirty-nine sedentary men and women (including 22 with the metabolic syndrome) had insulin responsiveness quantified using euglycemic clamps and underwent biopsies of the vastus lateralis muscle. Expression of insulin receptors, insulin receptor substrate-1 (IRS-1), GLUT4, and ATP synthase were quantified with immunoblots and immunohistochemistry.
Setting
An outpatient clinic.
Participants
Participants were non-diabetic, metabolic syndrome volunteers and sedentary control subjects.
Interventions
None.
Main Outcome Measures
Insulin responsiveness during an insulin clamp and the fiber composition of a muscle biopsy specimen.
Results
There were less Type I fibers and more mixed (Type IIa) fibers in metabolic syndrome subjects. Insulin responsiveness and maximal oxygen uptake correlated with the proportion of Type I fibers. Insulin receptor, IRS-1, and GLUT4 expression were not different in whole muscle but all were significantly less in the Type I fibers of metabolic syndrome subjects when adjusted for fiber proportion and fiber size. Fat oxidation and muscle mitochondrial expression were not different in the metabolic syndrome subjects.
Conclusion
Lower proportion of type I fibers in metabolic syndrome muscle correlated with the severity of insulin resistance. Even though whole muscle content was normal, key elements of insulin action were consistently less in type I muscle fibers, suggesting their distribution was important in mediating insulin effects.
小提示:本篇资讯需要登录阅读,点击跳转登录
版权声明:
本网站所有内容来源注明为“梅斯医学”或“MedSci原创”的文字、图片和音视频资料,版权均属于梅斯医学所有。非经授权,任何媒体、网站或个人不得转载,授权转载时须注明来源为“梅斯医学”。其它来源的文章系转载文章,或“梅斯号”自媒体发布的文章,仅系出于传递更多信息之目的,本站仅负责审核内容合规,其内容不代表本站立场,本站不负责内容的准确性和版权。如果存在侵权、或不希望被转载的媒体或个人可与我们联系,我们将立即进行删除处理。
在此留言
本网站所有内容来源注明为“梅斯医学”或“MedSci原创”的文字、图片和音视频资料,版权均属于梅斯医学所有。非经授权,任何媒体、网站或个人不得转载,授权转载时须注明来源为“梅斯医学”。其它来源的文章系转载文章,或“梅斯号”自媒体发布的文章,仅系出于传递更多信息之目的,本站仅负责审核内容合规,其内容不代表本站立场,本站不负责内容的准确性和版权。如果存在侵权、或不希望被转载的媒体或个人可与我们联系,我们将立即进行删除处理。
在此留言







#JCEM#
101
#胰岛#
59
#JCE#
50
#肌纤维#
68
#反应性#
95
#骨骼肌#
82