J. Neurosci.:发现转录因子c-Maf调控脊髓背角及背根神经节中机械感觉神经元的发育
2012-05-19 中科院 中科院
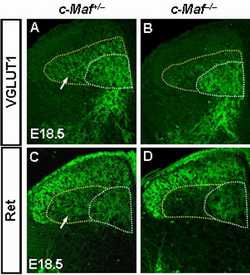
c-Maf–/–中RA机械感觉神经元向中枢脊髓背角III/IV层神经元的投射异常。 4月18号,《神经科学杂志》(The Journal of Neuroscience) 发表了中科院上海生科院神经所神经发育及其调控机理研究组的论文《c-Maf is required for the development of dorsal horn laminae III/IV neurons and me

c-Maf–/–中RA机械感觉神经元向中枢脊髓背角III/IV层神经元的投射异常。
4月18号,《神经科学杂志》(The Journal of Neuroscience) 发表了中科院上海生科院神经所神经发育及其调控机理研究组的论文《c-Maf is required for the development of dorsal horn laminae III/IV neurons and mechanoreceptive DRG axon projections》。该项工作是由博士研究生胡佳和黄天文等在程乐平研究员的指导下共同完成的。同期的The Journal of Neuroscience发表了题为“c-Maf 帮助决定RA传入纤维命运”(c-Maf Helps Specify RA Afferent Fate)的评论,对该项工作进行了介绍。
正常的躯体感觉依赖于外周背根神经节(DRG)及其投射区–脊髓背角神经元间建立精确的连接。机械刺激(包括物体质地、形状、振动及压力等信息)被外周感觉小体中的DRG机械感觉神经元接收,并向中枢投射至脊髓背角的III/IV层及脑形成触压觉。目前已知一些分子在脊髓背角神经元、感知痛觉及本体感觉的DRG神经元的发育中发挥重要作用。然而,关于参与形成触压觉的脊髓背角III/IV层神经元及DRG中低阈值的机械感觉神经元(low-threshold mechanoreceptor, LTM)的发育,目前的报道还很少。利用原位杂交及免疫组化染色等技术,作者发现转录因子c-Maf特异表达在脊髓背角的III/IV层神经元及背根神经节有髓鞘的中大直径神经元中。通过分析敲除小鼠的表型,发现c-Maf 调控脊髓背角III/IV层神经元的发育。进一步实验表明,c-Maf 基因敲除特异影响表达MafA、Ret及GFRα2的快适应性(rapidly adapting, RA)LTM的发育及其向中枢脊髓背角III/IV层神经元与外周帕西尼氏小体(Pacinian corpuscles)的投射。该研究结果揭示了转录因子c-Maf在脊髓背角III/IV层神经元发育、背根神经节RA LTM的发育及其投射建立中的重要作用。
该工作得到了科技部及中科院项目的资助。(生物谷:Bioon.com)

doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.6239-11.2012
PMC:
PMID:
c-Maf Is Required for the Development of Dorsal Horn Laminae III/IV Neurons and Mechanoreceptive DRG Axon Projections
Jia Hu, Tianwen Huang, Tingting Li, Zhen Guo, and Leping Cheng
Establishment of proper connectivity between peripheral sensory neurons and their central targets is required for an animal to sense and respond to various external stimuli. Dorsal root ganglion (DRG) neurons convey sensory signals of different modalities via their axon projections to distinct laminae in the dorsal horn of the spinal cord. In this study, we found that c-Maf was expressed predominantly in the interneurons of laminae III/IV, which primarily receive inputs from mechanoreceptive DRG neurons. In the DRG, c-Maf+ neurons also coexpressed neurofilament-200, a marker for the medium- and large-diameter myelinated afferents that transmit non-noxious information. Furthermore, mouse embryos deficient in c-Maf displayed abnormal development of dorsal horn laminae III/IV neurons, as revealed by the marked reduction in the expression of several marker genes for these neurons, including those for transcription factors MafA and Rora, GABAA receptor subunit α5, and neuropeptide cholecystokinin. In addition, among the four major subpopulations of DRG neurons marked by expression of TrkA, TrkB, TrkC, and MafA/GFRα2/Ret, c-Maf was required selectively for the proper differentiation of MafA+/Ret+/GFRα2+ low-threshold mechanoreceptors (LTMs). Last, we found that the central and peripheral projections of mechanoreceptive DRG neurons were compromised in c-Maf deletion mice. Together, our results indicate that c-Maf is required for the proper development of MafA+/Ret+/GFRα2+ LTMs in the DRG, their afferent projections in the dorsal horn and Pacinian corpuscles, as well as neurons in laminae III/IV of the spinal cord.
本网站所有内容来源注明为“梅斯医学”或“MedSci原创”的文字、图片和音视频资料,版权均属于梅斯医学所有。非经授权,任何媒体、网站或个人不得转载,授权转载时须注明来源为“梅斯医学”。其它来源的文章系转载文章,或“梅斯号”自媒体发布的文章,仅系出于传递更多信息之目的,本站仅负责审核内容合规,其内容不代表本站立场,本站不负责内容的准确性和版权。如果存在侵权、或不希望被转载的媒体或个人可与我们联系,我们将立即进行删除处理。
在此留言









#转录#
75
#背根神经#
69
#感觉神经#
61
#发育#
84
#ROS#
0
#转录因子#
83