手风琴征 / 屈曲征 (见于 CT 和 MRI ) 图像 脑外肿瘤(脑膜瘤) 讨论

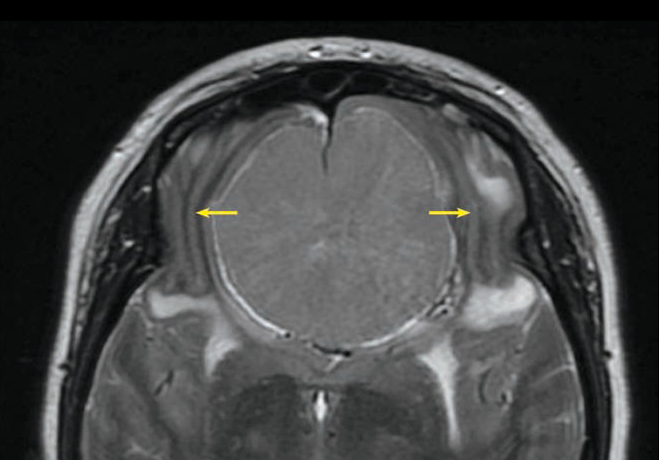
颅内肿块的正确定位对于准确的诊断和手术计划至关重要。脑内肿块扩大脑实质,并伴有周围血管性水肿。与脑内病变相比,脑外肿块移位并压迫邻近的大脑,伴脑回向内弯曲(“手风琴”或“屈曲”征),并且水肿较少。脑外肿瘤的其他有用表现包括“ CSF劈开”和“硬脑膜尾”征。脑膜瘤是最常见的脑外肿块,占所有脑肿瘤的15%。
FINDINGS:
Axial T2-weighted MR shows a mass in the anterior interhemispheric fi ssure, with surrounding T2-hyperintense rim. There is lateral displacement of the frontal lobe gyri (arrows) and mild vasogenic edema.
DIAGNOSIS:
Extraaxial mass (meningioma)
DISCUSSION:
Correct localization of an intracranial mass is crucial for accurate diagnosis and
surgical planning. Intraaxial masses expand the brain parenchyma, with surrounding vasogenic edema. Extraaxial masses displace and compress the adjacent brain, with inward bowing of gyri (“accordion” or “buckling” sign) and less edema than intraaxial lesions. Other useful fi ndings of an extraaxial mass include the “CSF cleft” and “dural tail” signs. Meningioma is the most common extraaxial mass, and comprises 15% of all brain tumors.
References
Drevelegas A. Extra-axial brain tumors. Eur Radiol. 2005;15(3):453-467.
George AE, Russell EJ, Kricheff II. White matter buckling: CT sign of extraaxial intracranial mass. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1980;135(5):1031-1036.
本网站所有内容来源注明为“梅斯医学”或“MedSci原创”的文字、图片和音视频资料,版权均属于梅斯医学所有。非经授权,任何媒体、网站或个人不得转载,授权转载时须注明来源为“梅斯医学”。其它来源的文章系转载文章,或“梅斯号”自媒体发布的文章,仅系出于传递更多信息之目的,本站仅负责审核内容合规,其内容不代表本站立场,本站不负责内容的准确性和版权。如果存在侵权、或不希望被转载的媒体或个人可与我们联系,我们将立即进行删除处理。
在此留言