髓外造血是骨髓红系造血功能衰竭的响应。髓外造血发生在血红蛋白病,骨髓增生性疾病或骨髓浸润性疾病。它大多发生在脾脏和肝脏,偶尔在淋巴结中出现。不常见的器官包括胸膜、肺、胃肠道、乳腺、皮肤、脑、肾和肾上腺。
Pathology
Aetiology
-
myeloproliferative disorders
-
chronic myelogenous leukemia
-
polycythemia vera
-
essential thrombocytosis
-
myelofibrosis with myeloid metaplasia
-
haemoglobinopathies
-
sickle cell disease
-
thalassemia
病理
病因
-
骨髓增生性疾病
.慢性粒细胞性白血病
.真性红细胞增多症
.原发性血小板增多症
.骨髓纤维化伴髓样化生
-
血红蛋白病
.镰状细胞病
-
地中海贫血
Radiographic features
Where extramedullary haematopoiesis involves an organ, there is usually radiographic evidence of its enlargement, e.g. hepatomegaly, splenomegaly visualised by ultrasound, CT or MRI. However, in the less common situation where extramedullary haematopoiesis involves other tissues within the thorax, they can be seen as aposterior mediastinal mass. These are paraspinal masses that may be unilateral or bilateral and have smooth, sharply delineated, often lobulated margins.
影像学特征
髓外造血器官,影像学上通常表现为器官增大,如超声、CT或MRI上表现为肝肿大、脾大。然而,在不常见的情况下,髓外造血可以发生在胸腔内,呈后纵隔肿块,变现为单侧或双侧脊柱旁肿块,边缘光滑,轮廓分明,常呈分叶状边缘。
病例图片:
图片来源:N Engl J Med 2010; 362:253
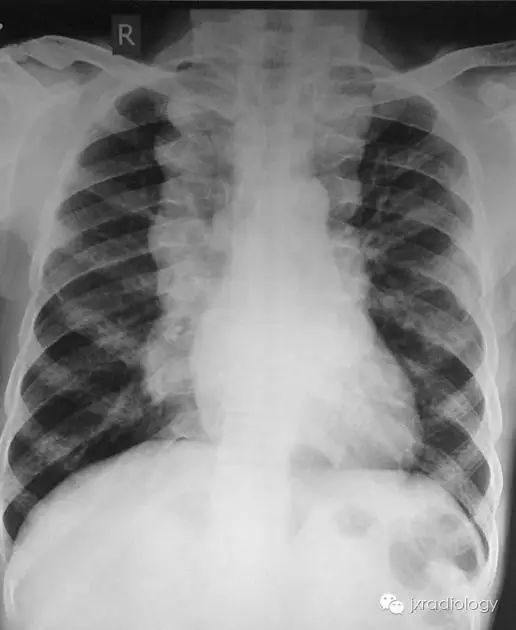
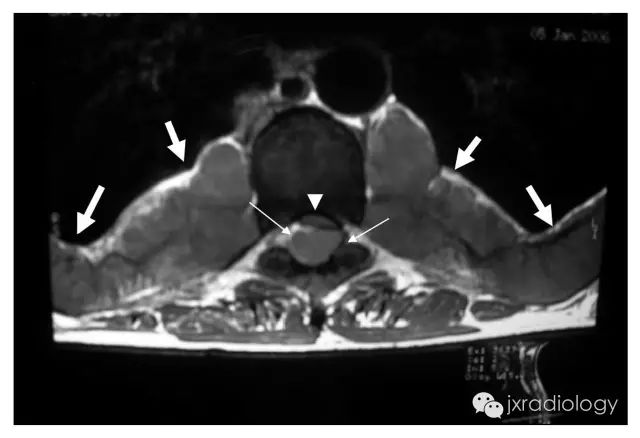
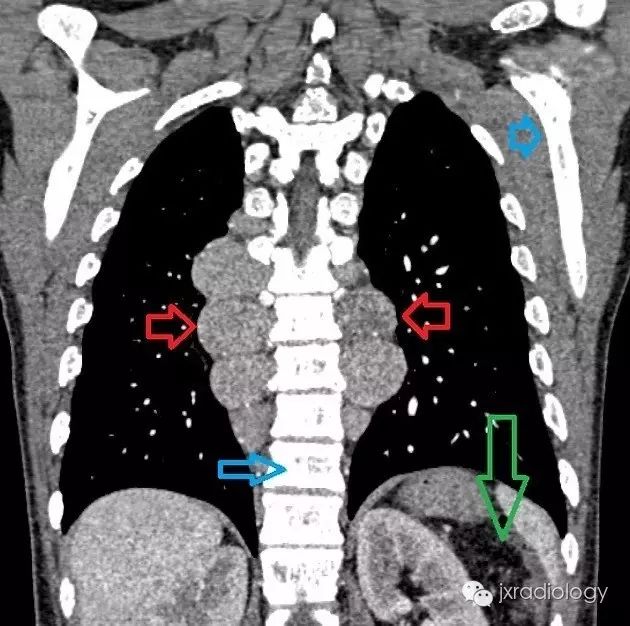
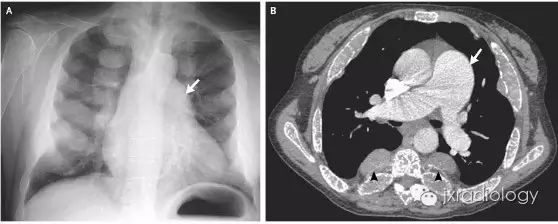
A 47-year-old woman of Italian descent with a history of transfusion-dependent β-thalassemia . Chest radiography (Panel A, arrow) and computed tomography (Panel B, arrow) show enlarged central pulmonary arteries owing to pulmonary arterial hypertension. In patients with thalassemia, such enlargement is thought to arise from chronic anemia, hemolysis, and an increased tendency for microscopic thrombi to form within the pulmonary vasculature. Bilateral paravertebral soft-tissue masses (Panel B, arrowheads), as well as marked medullary expansion of the bony structures (with the ribs showing the most pronounced involvement), were also present, findings that are associated with compensatory extramedullary hematopoiesis.
本网站所有内容来源注明为“梅斯医学”或“MedSci原创”的文字、图片和音视频资料,版权均属于梅斯医学所有。非经授权,任何媒体、网站或个人不得转载,授权转载时须注明来源为“梅斯医学”。其它来源的文章系转载文章,或“梅斯号”自媒体发布的文章,仅系出于传递更多信息之目的,本站仅负责审核内容合规,其内容不代表本站立场,本站不负责内容的准确性和版权。如果存在侵权、或不希望被转载的媒体或个人可与我们联系,我们将立即进行删除处理。
在此留言







