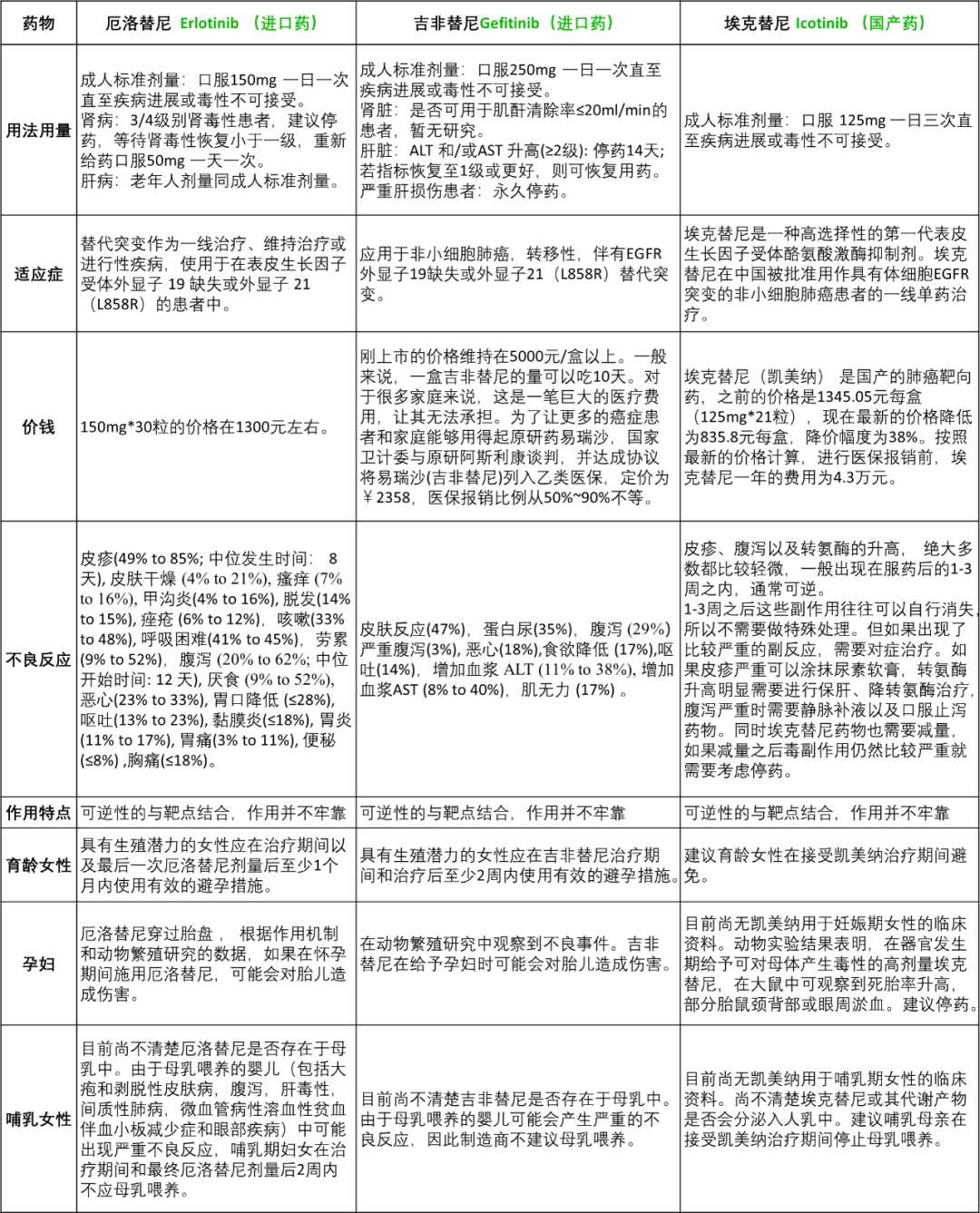
肺癌是全球癌症相关死亡的主要原因,总体五年生存率约为15%[1]。非小细胞肺癌(NSCLC)约占所有肺癌的75-80%[2]。当肿瘤局限于肺部并且区域淋巴结扩散最小时,最有效的治疗方法是手术。然而,约70% 的患者在诊断时表现为局部晚期或转移性疾病,不符合手术切除的条件。铂类化疗是晚期或复发性非小细胞肺癌的标准治疗方法,目前,患者反应率大约为30-40%。
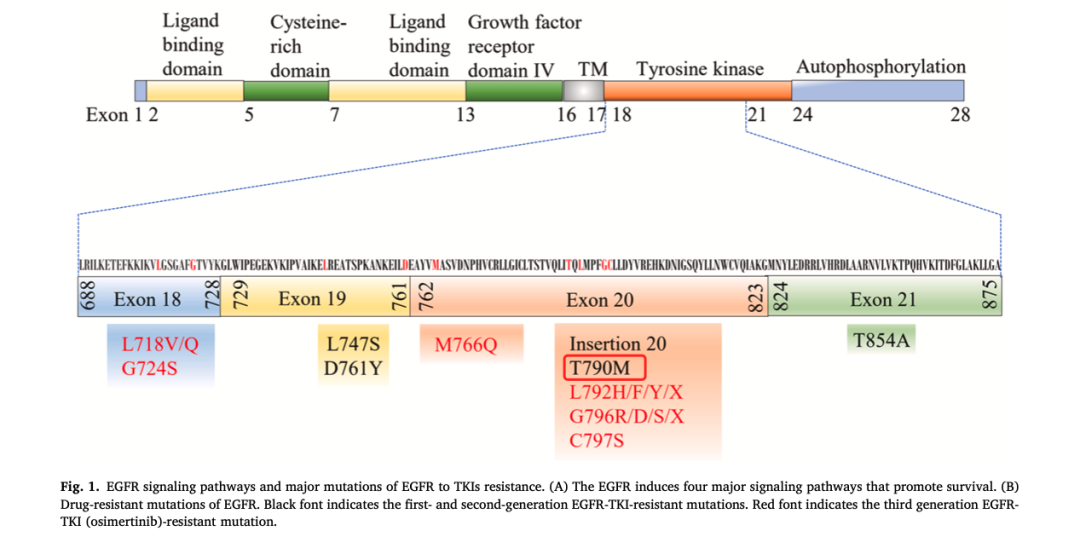
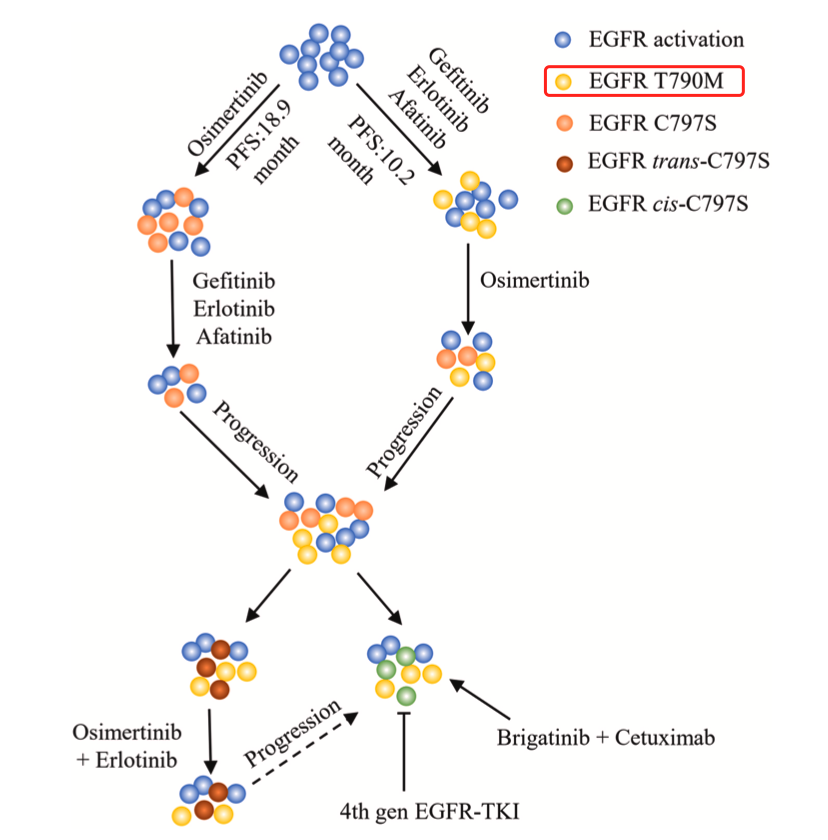
1、45-50% 为Exon 19删除, 40%为Exon 21 L858R点突变;
2、发病率: 白人10-15%, 亚洲人20-30%;
3、人群分布: 主要集中在非吸烟腺癌患者;
4、形成新的 T790M基因突变;
5、癌症类型转变: 在使用TKI药物的EGFR突变患者这可能会出现组织学转变,即非小细胞肺癌转变为小细胞肺癌;
6、免疫治疗通常对EGFR突变的患者无效。
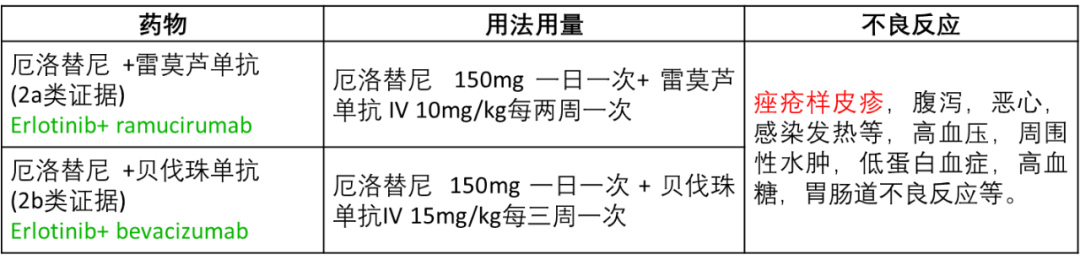


轻症: 甲硝唑膏剂;
中-重:四环素;
止痒: 抗组胺药物等。
Reference:
[1]. Visbal AL, Williams BA,Nichols FC 3rd, Marks RS, Jett JR, et al. 2004. Gender differences innonsmall-cell lung cancer survival: an analysis of 4618 patients diagnosedbetween 1997 and 2002. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 78:209–15
[2]. Travis WD, Brambilla E,Muller-Hemerlink WK, Harris CC, eds. 2004. Pathology and Genetics of Tumours ofthe Lung, Pleura, Thymus and Heart. Oxford, UK: Oxford Univ.
Press
[3]. Blackhall FH, Shepherd FA,Albain KS. 2005. Improving survival and reducing toxicity with chemotherapy inadvanced nonsmall cell lung cancer: a realistic goal? Treat. Respir. Med.4:71–84
[4]. Goldstraw P, Crowley J,Chansky K, Giroux DJ, Groome PA, et al. 2007. The IASLC Lung Cancer StagingProject: proposals for the revision of the TNM stage groupings in the forthcoming(seventh) edition of the TNM classification of malignant tumours. J. Thorac.Oncol. 2:706–14
[5]. Fukui T, Mori S, Hatooka S,Shinoda M, Mitsudomi T. 2008. Prognostic evaluation based on a new TNM stagingsystem proposed by the International Association for the Study of Lung Cancerfor resected nonsmall cell lung cancers. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg.136:1343–48
[6]. Dong RF, Zhu ML, Liu MM, XuYT, Yuan LL, Bian J, Xia YZ, Kong LY. EGFR mutation mediates resistance to EGFRtyrosine kinase inhibitors in NSCLC: From molecular mechanisms to clinicalresearch. Pharmacol Res. 2021 May;167:105583. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2021.105583.Epub 2021 Mar 26. PMID: 33775864.
[7] Y. Shi, S. Zhang, X. Hu, J. Feng, Z. Ma,J. Zhou, N. Yang, L. Wu, W. Liao,
D. Zhong, X. Han, Z. Wang, X. Zhang, S. Qin,K. Ying, J. Feng, J. Fang, L. Liu, Y. Jiang, Safety, clinical activity, andpharmacokinetics of Alflutinib (AST2818) in patients with advanced NSCLC withEGFR T790M mutation, J. Thorac. Oncol. 15 (6) (2020) 1015–1026,https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtho.2020.01.010.
[8] Y. Shi, X. Hu, S. Zhang, N. Yang, Y.Zhang, W. Li, X. Han, H. Mo, Y. Sun, P2.03- 028 third generation EGFR inhibitorAST2818 (Alflutinib) in NSCLC patients with EGFR T790M mutation: a phase1/2multi-center clinical trial, J. Thorac. Oncol. 12 (11) (2017),https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtho.2017.09.1279. S2138.
[9] Y. Shi, X. Hu, S. Zhang, D.Lv, Y. Zhang, Q. Yu, L. Wu, L. Liu, X. Wang, Z. Ma, Y. Cheng, H. Niu, D. Wang,J.F. Feng, C. Huang, C. Liu, H. Zhao, J. Li, X. Zhang, Y. Jiang, Efficacy andsafety of alflutinib (AST2818) in patients with T790M mutation-positive NSCLC:a phase IIb multicenter single-arm study, J. Clin. Oncol. 38 (15_suppl) (2020),https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2020.38.15_ suppl.9602, 9602.
[10] J. Yun, M.H. Hong, S.Y. Kim, C.W. Park,S. Kim, M.R. Yun, H.N. Kang, K.H. Pyo, S. S. Lee, J.S. Koh, H.J. Song, D.K.Kim, Y.S. Lee, S.W. Oh, S. Choi, H.R. Kim, B. C. Cho, YH25448, an irreversibleEGFR-TKI with potent intracranial activity in EGFR mutant non-small cell lungcancer, Clin. Cancer Res. 25 (8) (2019) 2575–2587,https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.Ccr-18-2906.
[11] M.H. Hong, I.Y. Lee, J.S. Koh, J. Lee,B.-C. Suh, H.-J. Song, P. Salgaonkar, J. Lee, Y.-S. Lee, S.-W. Oh, J.K. Kim,S.Y. Nam, B.C. Cho, P3.02b-119 YH25448, a highly selective 3rd generation EGFRTKI, exhibits superior survival over osimertinib in animal model with brainmetastases from NSCLC: topic: EGFR RES, J. Thorac. Oncol. 12 (1) (2017)S1265–S1266, https://doi.org/10.1016/j. jtho.2016.11.1787.
[12] M.J. Ahn, J.Y. Han, K.H. Lee,S.W. Kim, D.W. Kim, Y.G. Lee, E.K. Cho, J.H. Kim, G.W. Lee, J.S. Lee, Y.J. Min,J.S. Kim, S.S. Lee, H.R. Kim, M.H. Hong, J.S. Ahn, J. M. Sun, H.T. Kim, D.H.Lee, S. Kim, B.C. Cho, Lazertinib in patients with EGFR mutation-positiveadvanced non-small-cell lung cancer: results from the dose escalation and doseexpansion parts of a first-in-human, open-label, multicentre, phase 1-2 study,Lancet Oncol. 20 (12) (2019) 1681–1690, https://doi.org/10.1016/s1470-2045(19)30504-2.
[13] X. Xu, Parallel phase 1 clinical trialsin the US and in China: accelerating the test of avitinib in lung cancer as anovel inhibitor selectively targeting mutated EGFR and overcoming T790M-inducedresistance, Chin. J. Cancer 34 (7) (2015) 285–287,https://doi.org/10.1186/s40880-015-0029-3.
[14] X. Xu, L. Mao, W. Xu, W. Tang, X. Zhang,B. Xi, R. Xu, X. Fang, J. Liu, C. Fang, L. Zhao, X. Wang, J. Jiang, P. Hu, H.Zhao, L. Zhang, AC0010, an Irreversible EGFR inhibitor selectively targetingmutated EGFR and overcoming T790M- induced resistance in animal models and lungcancer patients, Mol. Cancer Ther. 15 (11) (2016) 2586–2597,https://doi.org/10.1158/1535-7163.Mct-16-0281.
[15] Y.L. Wu, Q. Zhou, X. Liu, L.Zhang, J. Zhou, L. Wu, T. An, Y. Cheng, X. Zheng, B. Hu, J. Jiang, X. Fang, W.Xu, X. Xu, MA16.06 phase I/II study of AC0010, mutant-selective EGFR inhibitor,in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients with EGFR T790M mutation, J.Thorac. Oncol. 12 (1) (2017) S437–S438, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtho.2016.11.510.
[16] Y. Ma, X. Zheng, H. Zhao, W. Fang, Y.Zhang, J. Ge, L. Wang, W. Wang, J. Jiang, S. Chuai, Z. Zhang, W. Xu, X. Xu, P.Hu, L. Zhang, First-in-human phase I study of AC0010, a mutant-selective EGFRinhibitor in non-small cell lung cancer: safety, efficacy, and potentialmechanism of resistance, J. Thorac. Oncol. 13 (7) (2018) 968–977, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtho.2018.03.025.
[17] H. Wang, L. Zhang, P. Hu, X. Zheng, X.Si, X. Zhang, M. Wang, Penetration of the blood-brain barrier by avitinib andits control of intra/extra-cranial disease in non-small cell, Lung Cancer 122(2018) 1–6, https://doi.org/10.1016/j. lungcan.2018.05.010.
[18] H. Wang, L. Zhang, X. Zheng,X. Si, X. Cui, M. Wang, P2.03-041 the concentration of avitinib in cerebrospinalfluid and its efficacy and safety in NSCLC patients with T790M mutation, J.Thorac. Oncol. 12 (11) (2017), https://doi.org/ 10.1016/j.jtho.2017.09.1292.S2143.
[19] X. Liu, X. Zhang, L. Yang, X. Tian, T.Dong, C.Z. Ding, L. Hu, L. Wu, L. Zhao,
J. Mao, Abstract 1320: preclinicalevaluation of TQB3804, a potent EGFR C797S inhibitor, Cancer Res. 79 (2019),1320, https://doi.org/10.1158/1538-7445. AM2019-1320.
本网站所有内容来源注明为“梅斯医学”或“MedSci原创”的文字、图片和音视频资料,版权均属于梅斯医学所有。非经授权,任何媒体、网站或个人不得转载,授权转载时须注明来源为“梅斯医学”。其它来源的文章系转载文章,或“梅斯号”自媒体发布的文章,仅系出于传递更多信息之目的,本站仅负责审核内容合规,其内容不代表本站立场,本站不负责内容的准确性和版权。如果存在侵权、或不希望被转载的媒体或个人可与我们联系,我们将立即进行删除处理。
在此留言











#不良反应#
103
#GFR#
76
感谢分享
75
学习了,感谢分享
86