Nature—人工耳蜗研究重磅突破:刺激蓝斑核可增强人工耳蜗对听力的恢复效果
2023-01-19 神经科学临床和基础 神经科学临床和基础 发表于安徽省
人工耳蜗的研究突破

英文摘要
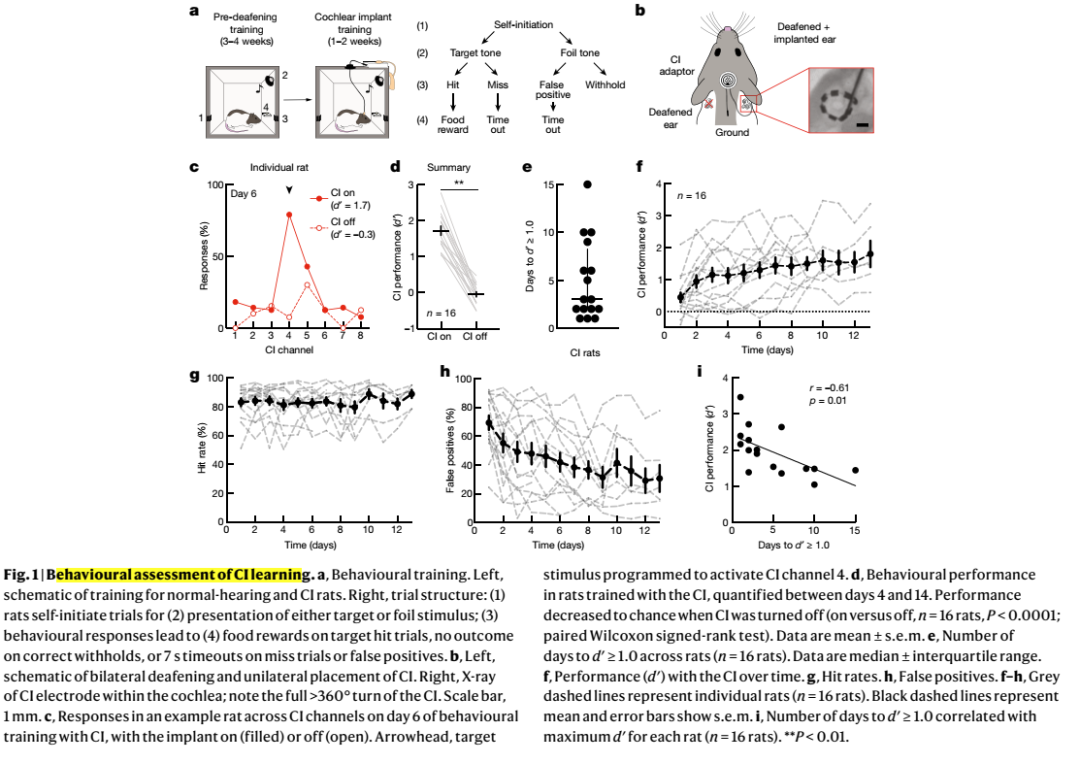
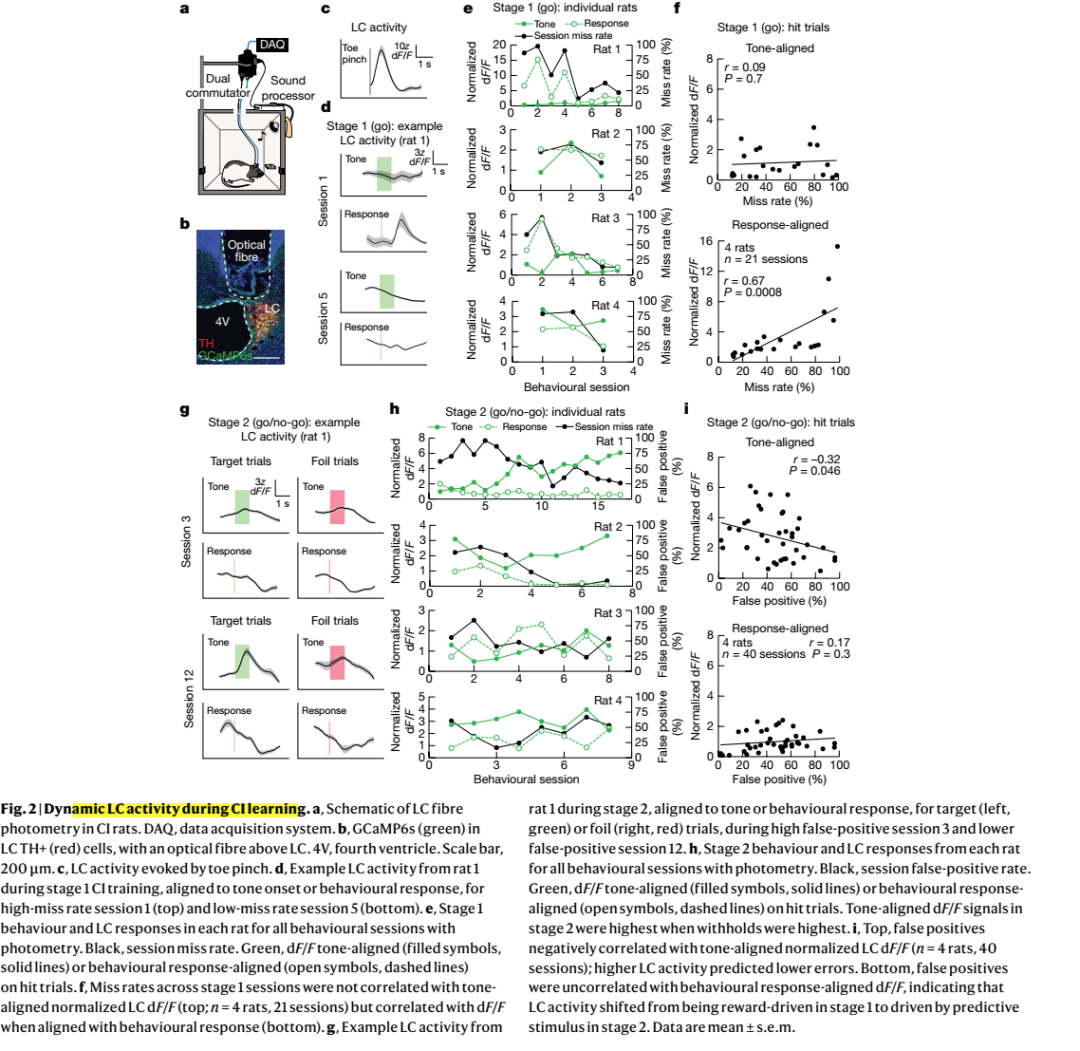
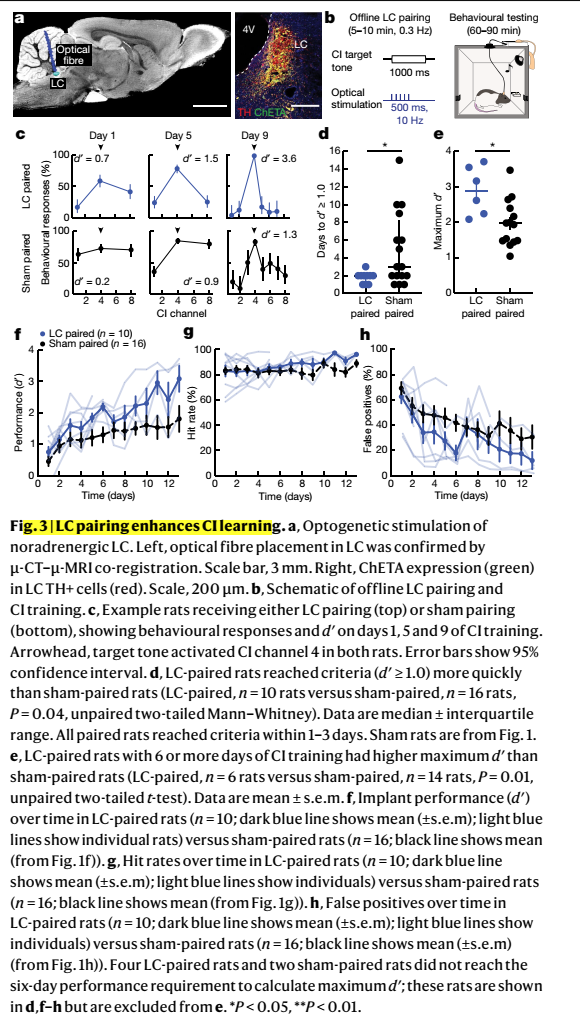
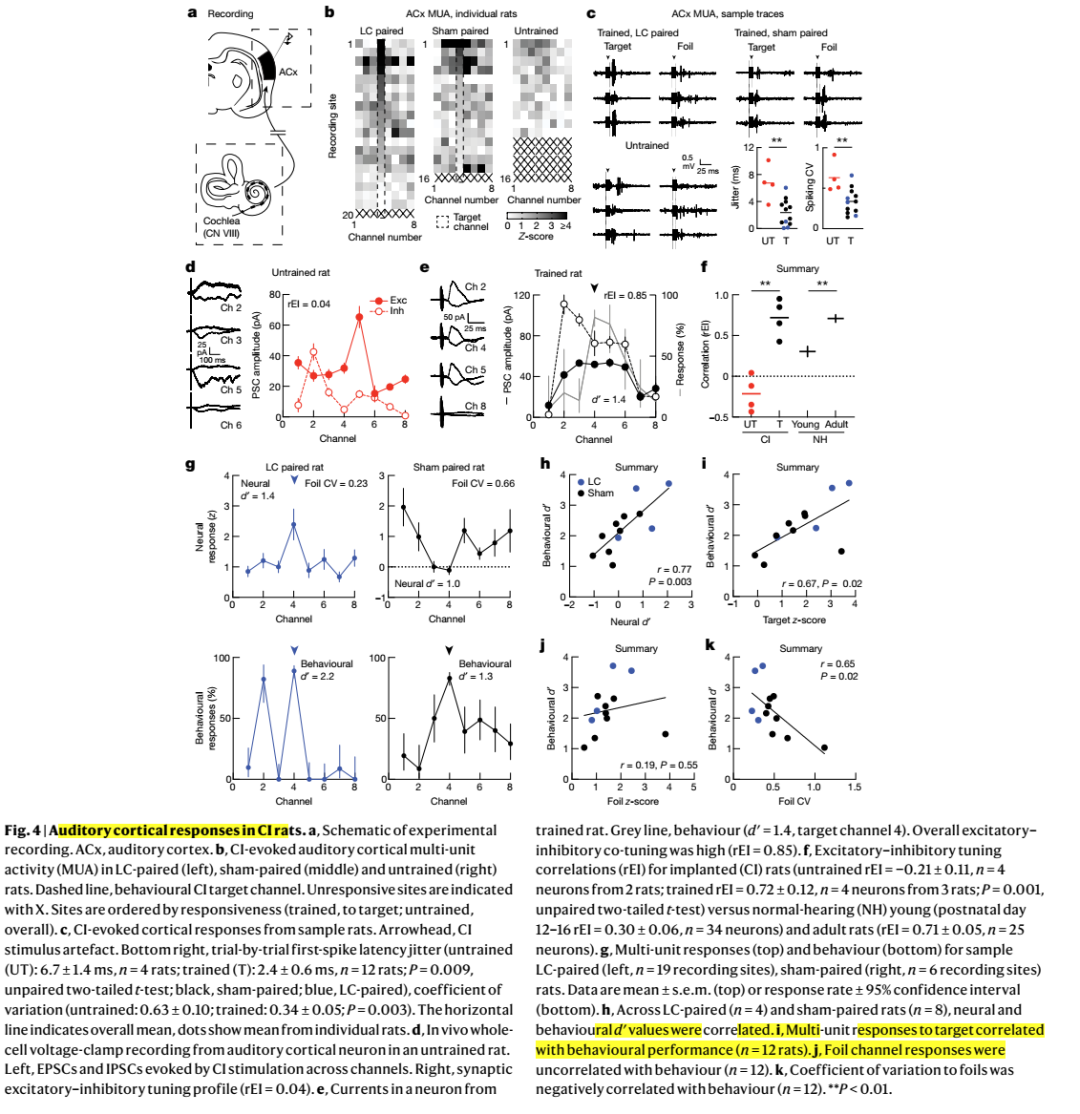
Cochlear implants (CIs) are neuroprosthetic devices that can provide hearing to deaf people1. Despite the benefits offered by CIs, the time taken for hearing to be restored and perceptual accuracy after long-term CI use remain highly variable2,3. CI use is believed to require neuroplasticity in the central auditory system, and differential engagement of neuroplastic mechanisms might contribute to the variability in outcomes4-7. Despite extensive studies on how CIs activate the auditory system4,8-12, the understanding of CI-related neuroplasticity remains limited. One potent factor enabling plasticity is the neuromodulator noradrenaline from the brainstem locus coeruleus (LC). Here we examine behavioural responses and neural activity in LC and auditory cortex of deafened rats fitted with multi-channel CIs. The rats were trained on a reward-based auditory task, and showed considerable inpidual differences of learning rates and maximum performance. LC photometry predicted when CI subjects began responding to sounds and longer-term perceptual accuracy. Optogenetic LC stimulation produced faster learning and higher long-term accuracy. Auditory cortical responses to CI stimulation reflected behavioural performance, with enhanced responses to rewarded stimuli and decreased distinction between unrewarded stimuli. Adequate engagement of central neuromodulatory systems is thus a potential clinically relevant target for optimizing neuroprosthetic device use.
本网站所有内容来源注明为“梅斯医学”或“MedSci原创”的文字、图片和音视频资料,版权均属于梅斯医学所有。非经授权,任何媒体、网站或个人不得转载,授权转载时须注明来源为“梅斯医学”。其它来源的文章系转载文章,或“梅斯号”自媒体发布的文章,仅系出于传递更多信息之目的,本站仅负责审核内容合规,其内容不代表本站立场,本站不负责内容的准确性和版权。如果存在侵权、或不希望被转载的媒体或个人可与我们联系,我们将立即进行删除处理。
在此留言