Blood:美科学家在急性白血病患者中发现microRNA预后指标
2012-05-19 T.Shen 生物谷
近日,来自美国俄亥俄州立大学的研究者在某些急性白血病病人中识别出了一种新的独立性的预后指标-microRNA-3151(miR-3151),这些白血病病人(CN-AML)都患有急性的髓样白血病并且其染色体都看似正常。研究者们发现当miR-3151在CN-AML高表达的时候,疾病对于相应的疗法并不奏效,而且病人的存活率比较低,这种效应与其它细胞中的基因突变并无任何联系。另外,miR-3151是由BA

近日,来自美国俄亥俄州立大学的研究者在某些急性白血病病人中识别出了一种新的独立性的预后指标-microRNA-3151(miR-3151),这些白血病病人(CN-AML)都患有急性的髓样白血病并且其染色体都看似正常。研究者们发现当miR-3151在CN-AML高表达的时候,疾病对于相应的疗法并不奏效,而且病人的存活率比较低,这种效应与其它细胞中的基因突变并无任何联系。另外,miR-3151是由BAALC基因编码,是一个病人由于miR-3151高表达引起的低生存率的一个独立的标记物。
研究者的研究成果刊登在了近日的杂志Blood上,文章中,研究者揭示了AML的本质特征,并且提出了未来治疗AML的有效疗法。研究者Clara D.Bloomfield博士表示,机体miR-3151和BAALC水平都高的患者相比其中一个水平高或者两者水平都低的患者结果并不理想,高水平的miR-3151和BAALC可以通过机体的不同机制来加重CN-AML病人的病情。这项研究中的研究对象为179名60岁的老年CN-AML患者。
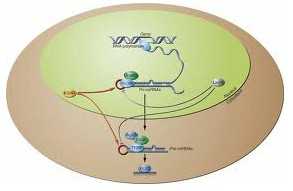
MicroRNAs是细胞中的小分子,可以帮助调节细胞中不同种类的大量蛋白质的代谢,人类1/3的microRNAs都是由持家基因所编码的,很特殊的是,这些小RNA是内含子的一部分,当遗传基因编码形成蛋白质以后,这些小段的DNA将不会被使用了。目前对于坐落在内含子部位的microRNAs的调节功能并不清楚,尤其是其涉及的持家基因间的反应更不清楚。
研究者Eisfeld表示,这是第一次我们阐述癌基因和内含子(有可能是致癌性的microRNA)之间的相互作用,这也是我们首次在白血病患者中发现重要的内含子microRNAs。相关研究由国家癌症中心等机构资助。(生物谷:T.Shen编译)

doi:10.1182/blood-2012-02-408492
PMC:
PMID:
miR-3151 interplays with its host gene BAALC and independently impacts on outcome of patients with cytogenetically normal acute myeloid leukemia
Ann-Kathrin Eisfeld1, Guido Marcucci1, Kati Maharry2, Sebastian Schwind1, Michael D. Radmacher1, Deedra Nicolet1, Heiko Becker1, Krzysztof Mrózek1, Susan P. Whitman1, Klaus H. Metzeler1, Jason H. Mendler1, Yue-Zhong Wu1, Sandya Liyanarachchi1, Ravi Patel1, Maria R. Baer3, Bayard L. Powell4, Thomas H. Carter5, Joseph O. Moore6, Jonathan E. Kolitz7, Meir Wetzler8, Michael A. Caligiuri1, Richard A. Larson9, Stephan M. Tanner1, Albert de la Chapelle1, and Clara D. Bloomfield1,*
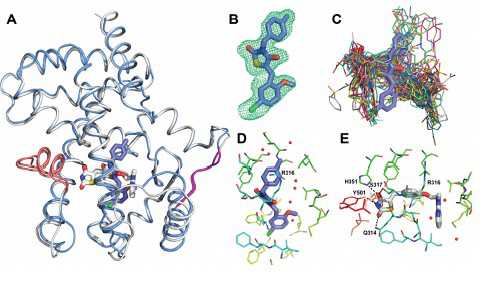
High BAALC expression levels associate with poor outcome in cytogenetically normal AML (CN-AML) patients. Recently, microRNA miR-3151 was discovered in intron 1 of BAALC. To evaluate the prognostic significance of miR-3151 expression levels and to gain insight into the biologic and prognostic interplay between miR-3151 and its host, miR-3151 and BAALC expression were measured in pretreatment blood of 179 CN-AML patients. Gene- (GEP) and microRNA-expression (MEP) profiling was performed using microarrays. High miR-3151 expression associated with shorter disease-free and overall survival, while high BAALC expression predicted failure of complete remission and shorter overall survival. Patients exhibiting high expression of both miR-3151 and BAALC had worse outcome than patients expressing low levels of either gene or both genes. In GEP high miR-3151 expressers showed downregulation of genes involved in transcriptional regulation, post-translational modification and cancer pathways. Two genes, FBXL20 and USP40, were validated as direct miR-3151 targets. In conclusion, high expression of miR-3151 is an independent prognosticator for poor outcome in CN-AML and impacts on different outcome endpoints than its host gene BAALC. The combination of both markers identified a patient subset with the poorest outcome. The described interplay of an intronic miR and its host may have important biologic implications.
本网站所有内容来源注明为“梅斯医学”或“MedSci原创”的文字、图片和音视频资料,版权均属于梅斯医学所有。非经授权,任何媒体、网站或个人不得转载,授权转载时须注明来源为“梅斯医学”。其它来源的文章系转载文章,或“梅斯号”自媒体发布的文章,仅系出于传递更多信息之目的,本站仅负责审核内容合规,其内容不代表本站立场,本站不负责内容的准确性和版权。如果存在侵权、或不希望被转载的媒体或个人可与我们联系,我们将立即进行删除处理。
在此留言








#CRO#
62
#Micro#
81
#预后指标#
83
#microRNA#
58