AIP Advances:新突破---利用脉冲光声技术检测人体少量癌细胞
2012-04-09 towersimper 生物谷
为了在疾病早期阶段或者接受治疗后能够检测到病人体内存在的癌细胞,科学家们已经开发出很多种技术和方法。但是这些技术的一个主要限制因素就是当只有少数癌细胞存在时,它们就无法检测到。 脉冲光声技术(pulsed photoacoustic technique)将光学断层成像(optical tomography)的高光学对比度和超声波的高分辨率特征结合在一起。如今,来自美国密苏里大学哥伦比亚分校(Un

为了在疾病早期阶段或者接受治疗后能够检测到病人体内存在的癌细胞,科学家们已经开发出很多种技术和方法。但是这些技术的一个主要限制因素就是当只有少数癌细胞存在时,它们就无法检测到。
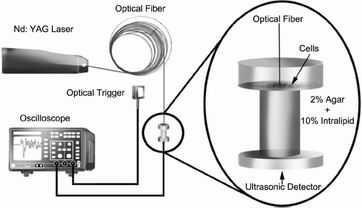
脉冲光声技术(pulsed photoacoustic technique)将光学断层成像(optical tomography)的高光学对比度和超声波的高分辨率特征结合在一起。如今,来自美国密苏里大学哥伦比亚分校(University of Missouri-Columbia)和墨西哥瓜纳华托大学(Universidad de Guanajuato)的研究人员合作完成的一项研究表明利用脉冲光声技术就能够在体外检测到人体内存在的少量癌细胞。因为大多数癌细胞通常难以捕捉,所以研究人员使用一种光声增强剂(photoacoustic enhancer)来检测它们。
研究人员说,开发新的检测方法是必需的。如今他们能够合适地使用脉冲光声技术来识别人体血液或组织样品中存在的不同类型癌细胞。相关研究结果于2012年3月19日发表在AIP Advances期刊上。(生物谷:towersimper编译)

doi:10.1063/1.3697852
PMC:
PMID:
An experimental and theoretical approach to the study of the photoacoustic signal produced by cancer cells
Rafael Pérez Solano, Francisco I. Ramirez-Perez, Jorge A. Castorena-Gonzalez, Edgar Alvarado Anell, Gerardo Gutiérrez-Juárez, and Luis Polo-Parada
The distinctive spectral absorption characteristics of cancer cells make photoacoustic techniques useful for detection in vitro and in vivo. Here we report on our evaluation of the photoacoustic signal produced by a series of monolayers of different cell lines in vitro. Only the melanoma cell line HS936 produced a detectable photoacoustic signal in which amplitude was dependent on the number of cells. This finding appears to be related to the amount of melanin available in these cells. Other cell lines (i.e. HL60, SK-Mel-1, T47D, Hela, HT29 and PC12) exhibited values similar to a precursor of melanin (tyrosinase), but failed to produce sufficient melanin to generate a photoacoustic signal that could be distinguished from background noise. To better understand this phenomenon, we determined a formula for the time-domain photoacoustic wave equation for a monolayer of cells in a non-viscous fluid on the thermoelastic regime. The theoretical results showed that the amplitude and profile of the photoacoustic signal generated by a cell monolayer depended upon the number and distribution of the cells and the location of the point of detection. These findings help to provide a better understanding of the factors involved in the generation of a photoacoustic signal produced by different cells in vitro and in vivo.
本网站所有内容来源注明为“梅斯医学”或“MedSci原创”的文字、图片和音视频资料,版权均属于梅斯医学所有。非经授权,任何媒体、网站或个人不得转载,授权转载时须注明来源为“梅斯医学”。其它来源的文章系转载文章,或“梅斯号”自媒体发布的文章,仅系出于传递更多信息之目的,本站仅负责审核内容合规,其内容不代表本站立场,本站不负责内容的准确性和版权。如果存在侵权、或不希望被转载的媒体或个人可与我们联系,我们将立即进行删除处理。
在此留言









#新突破#
107
#癌细胞#
97