肥胖,美国在研基金简述(2024)
2024-09-18 Hanson临床科研 Hanson临床科研 发表于上海
我们仅对美国国立卫生研究院(NIH)资助的在研肥胖相关项目进行梳理,希望给同仁们的选题思路提供一点启发。
肥胖(Obesity)是一种涉及过多体脂积累的慢性疾病,可能对健康造成严重影响。它通常通过身体质量指数(BMI)来定义和分类,BMI 是体重(公斤)除以身高(米)的平方。成人的BMI 等于或大于30时通常被诊断为肥胖。
尽管近年来在肥胖的诊断和治疗方面取得了显著进展,但仍存在一些重要而未解决的临床问题:
-
筛查和诊断:尽管有广泛的筛查程序,但许多人仍未被诊断出高血压。缺乏症状常使得患者忽视血压的定期检测,导致病情恶化后才被发现。
-
治疗方法的有效性:尽管有多种减重方法,如生活方式改变、药物治疗和外科手术,许多肥胖患者难以长期维持体重减轻。
-
个体化治疗:不同患者对治疗的反应差异大,需要更多研究来确定如何为不同的患者群体定制最有效的治疗方案。
-
预防策略:有效的公共健康策略和干预措施,用于预防肥胖的发生和发展,仍然是一个挑战。
-
肥胖相关并发症的管理:肥胖相关的并发症广泛,如心血管疾病、糖尿病、肌肉骨骼疾病等,如何有效管理这些并发症是一个持续的挑战。
-
社会和心理因素:肥胖患者常常面临社会歧视和心理压力,这些因素可以影响他们的治疗结果和生活质量。
解决这些问题需要综合的方法,包括更好的公共健康政策、更有效的治疗方案、以及针对肥胖和其并发症的新研究。同时,增强公众对肥胖严重性的认识和理解,也是改善这一全球性健康问题的关键步骤。
我们仅对美国国立卫生研究院(NIH)资助的在研肥胖相关项目进行梳理,希望给同仁们的选题思路提供一点启发。
2024年,以“Obesity”为检索词、在题目中进行检索,美国NIH针对肥胖的在研有648项。
一,谁获得了这些研究?
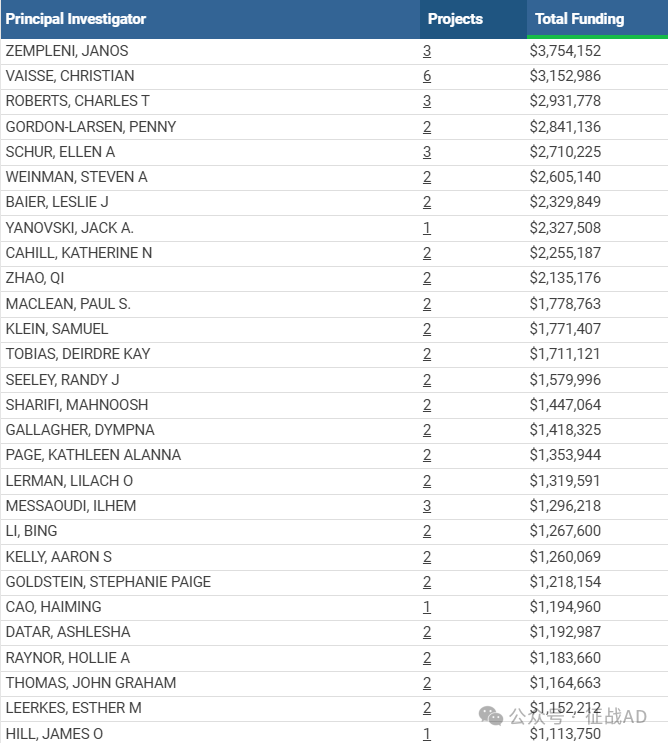
1,在研肥胖基金最多的PI
-
UNIVERSITY OF NEBRASKA LINCOLN 的 ZEMPLENI, JANOS
-
UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA, SAN FRANCISCO 的 VAISSE, CHRISTIAN
-
OREGON HEALTH & SCIENCE UNIVERSITY 的 ROBERTS, CHARLES T
-
UNIV OF NORTH CAROLINA CHAPEL HILL 的 GORDON-LARSEN, PENNY
-
UNIVERSITY OF WASHINGTON 的 SCHUR, ELLEN A
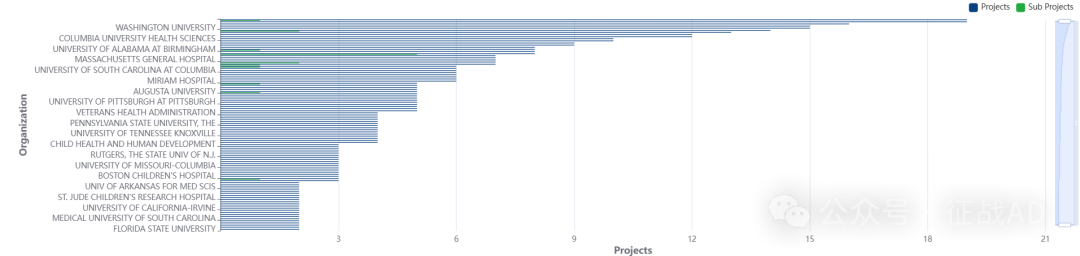
2,肥胖课题最多的研究机构
-
北卡罗来纳大学教堂山分校
-
科罗拉多大学丹佛分校
-
耶鲁大学
-
明尼苏达大学
-
华盛顿大学等
二,肥胖研究热点是什么?
肥胖研究领域总览(根据关键词)
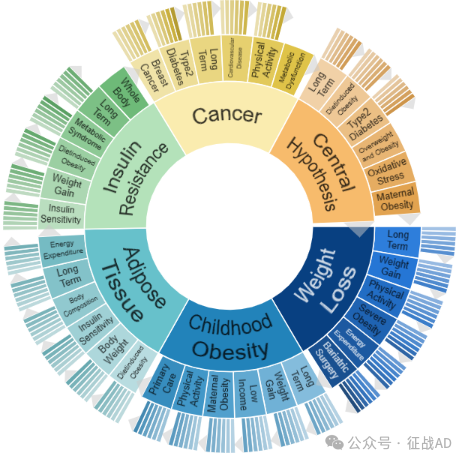
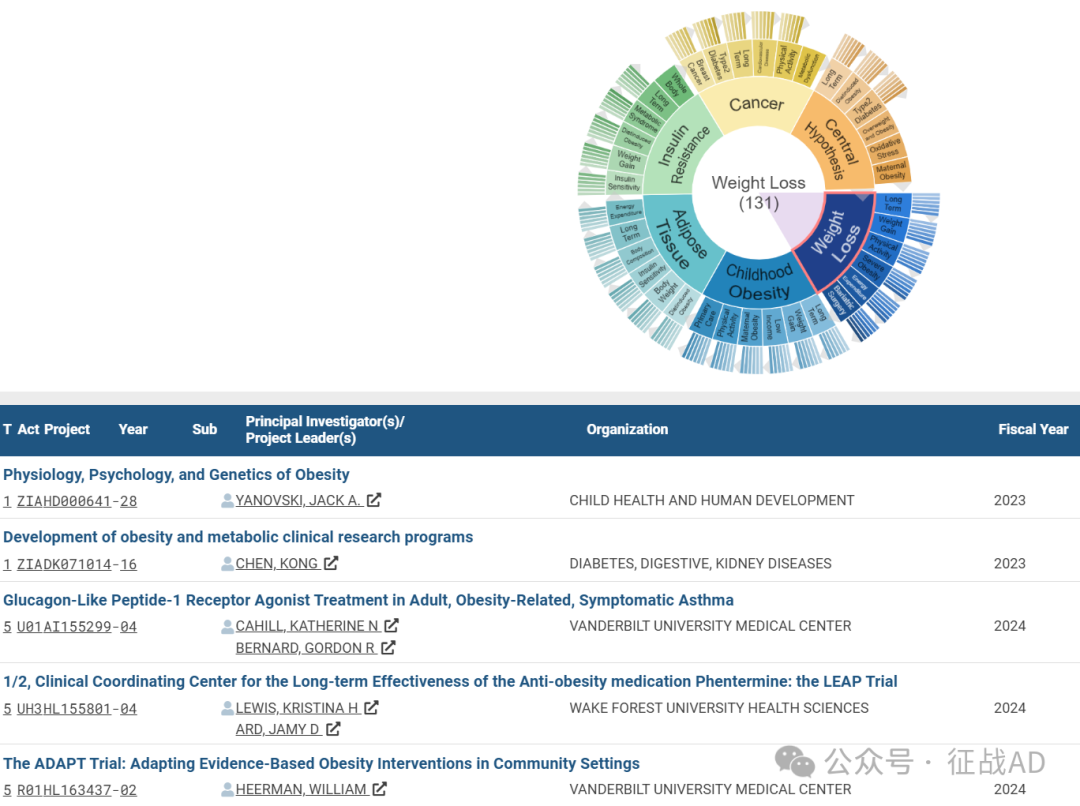
A,关于减重(Weight Loss)的研究项目最多
有 131 项在研基金涉及到了减重,关注最多的方面包括长期(Long Term)、体重增加(Weight Gain)、运动(Physical Activity)、严重肥胖(Severe Obesity)、能量消耗(Energy Expenditure)、减肥手术(Bariatiric Surgery)等研究。
B,儿童肥胖(Childhood Obesity)的研究
有 105 项研究涉及到儿童肥胖,研究领域主要涉及长期(Long Term)、体重增加(Weight Gain)、低收入(Low Income)、孕产妇肥胖(Maternal Obesity)、运动(Physical Activity)、初级保健(Primary Care)方面研究。
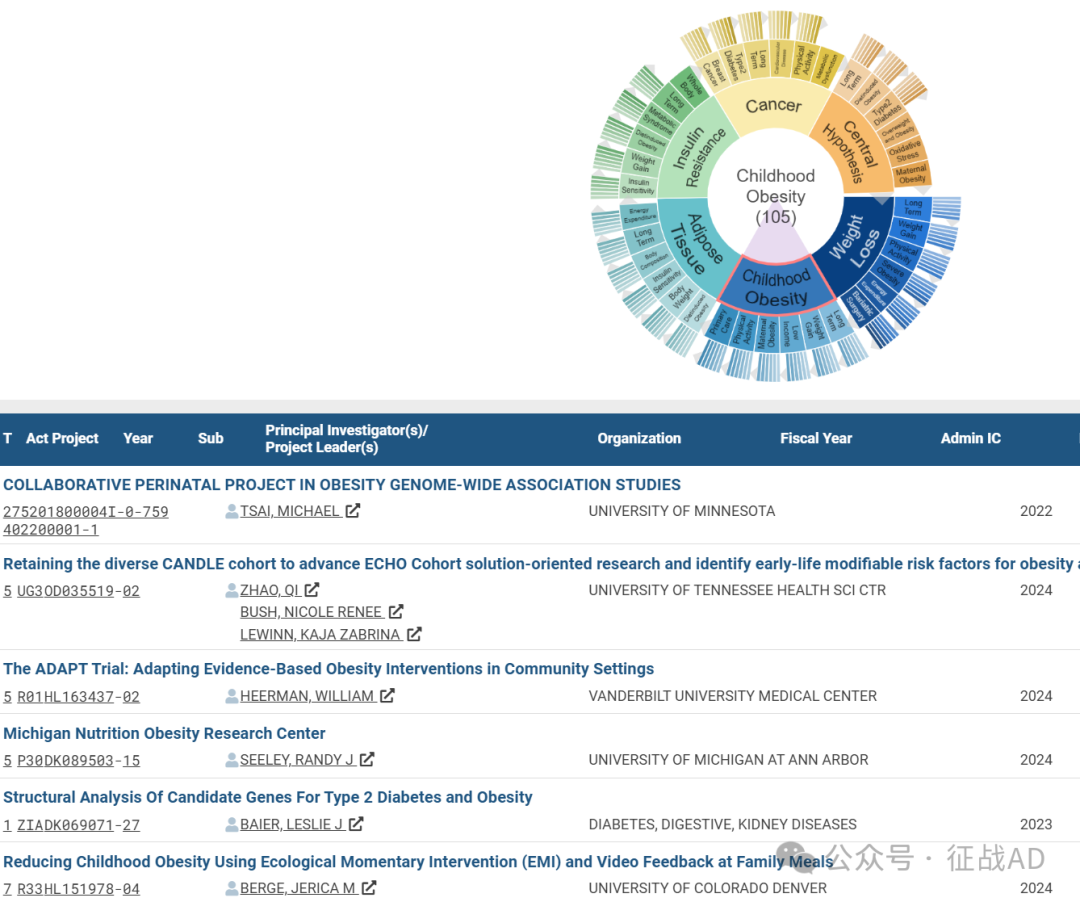
C,脂肪组织(Adipose Tissue)
有 85 项研究涉及到脂肪组织,涉及的关键词包括饮食引起的肥胖(Dietinduced Obesity)、体重(Body Weight)、胰岛素敏感性(Insulin Sensitivity)、(Body Composition)、长期(Long Term)、、能量消耗(Energy Expenditure)等。
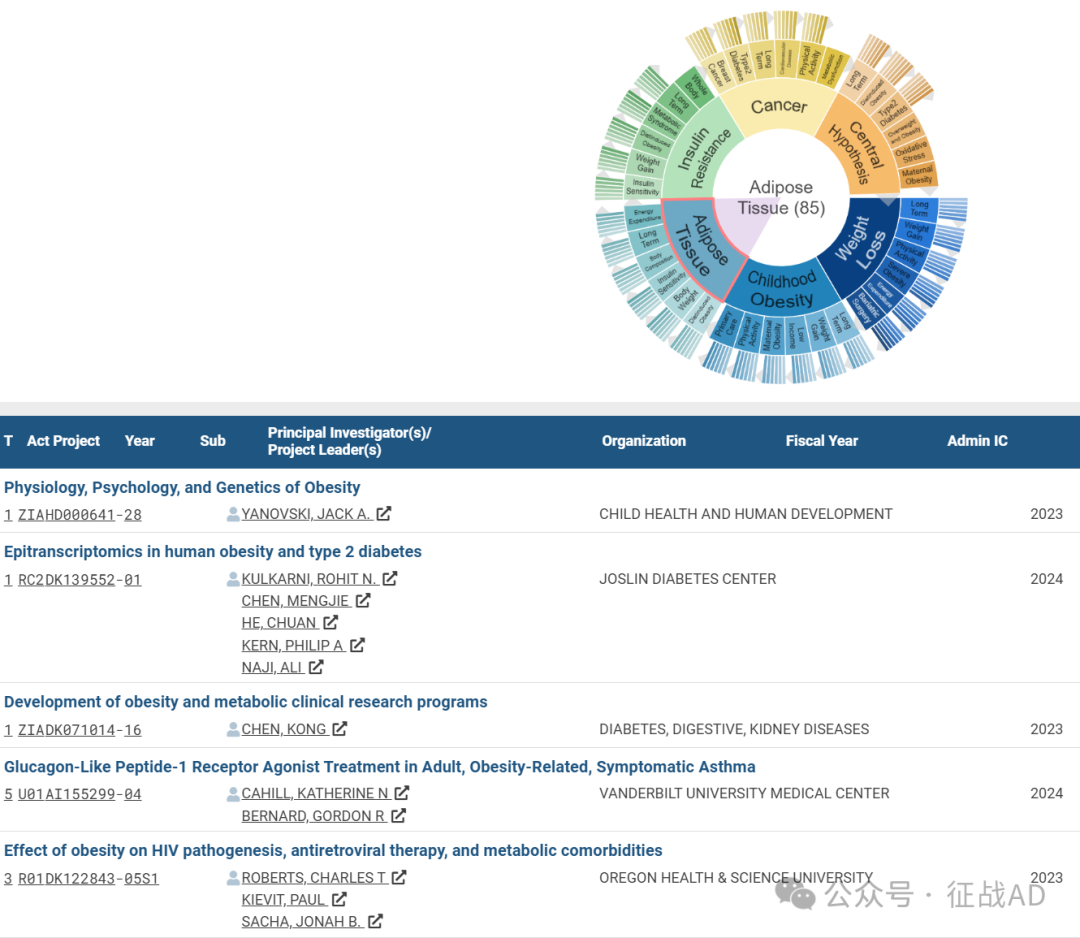
其他肥胖研究大的方向也包括胰岛素抵抗(Insulin Resistance)、癌症(Cancer)、中心假设(Central Hypothesis)等。
三,借鉴与突破
我们也分享在肥胖领域的几项课题摘要,希望对同仁们有所启发。
A,Kansas Center for Metabolism and Obesity REsearch (KC-MORE)
The KC- MORE will serve to merge these areas of focus by (1) creating a shared intellectual home for obesity-related researchers through a common educational and seminar program, (2) providing funding and mentorship for early stage obesity-related investigators to establish independent research careers, (3) establishing scientific cores to facilitate translational research of both early stage and established investigators, and (4) partnering with departments to jointly recruit new investigators to KUMC focused on themes of the KC-MORE.
The KC-MORE will be led by two multi- PIs, Drs. Steven Weinman and John Thyfault, and a renowned senior investigator, Dr. Joseph Donnelly who will serve as Chair of the Steering Committee and lead human energy balance research. These leaders have multi- disciplinary but complimentary expertise in basic, clinical, and translational research.
Phase 1 of the Center will support the development of four Research Project Leaders (RPLs) with studies on neural control of energy balance, clinical-based approaches to weight loss in rural communities, and basic mechanisms of obesity-related fatty liver disease and hypertension.
The KC-MORE will lead 3 new scientific cores that provide a foundation for translational research capabilities (the Metabolism (MET) core, the Cells, Tissues, Bioanalysis and Bioinformatics (CTBB) core, and the Human Energy Balance (HEB) core).
A critical goal of phase 1 of the KC-MORE COBRE will be to help RPLs develop independent, R01-funded research programs.
B, Development of a Novel Hyaluronan Inhibitor for the Treatment of Group 3 Pulmonary Hypertension (PH)
Consistent with the requirement of a RC2 mechanism, we will develop a comprehensive database of functionally important RNA modifications in selected human tissues. We seek to interrogate alterations in the modifications of RNA, specifically, the two most important modifications, N6-adenosine methylation (m6A) and pseudouridylation in key metabolic cell types that are relevant for type 2 diabetes and obesity.
In this proposal, we will:
1) Interrogate the mRNA and chromatin- associated RNA modifications, m6A-sequencing and BID-ψ-sequencing at base resolution with stoichiometry information in key metabolic tissues from patients with T2D and obesity;
2) Perform m6A and ψ QTL studies in tissues from patients with T2D and obesity and validate the functional relevance of key mRNA and chromatin- associated RNA modifications in in vitro studies;
3) Interrogate comprehensive transcription and enhancer activity using ATAC-seq in the metabolic tissues from patients with T2D and obesity;
4) Perform eQTL studies using transcriptional activity data obtained from KAS-seq and RNA modification results on carRNAs in T2D and obese tissues, and perform validation in in vitro studies;
5) Develop a large-scale resource database on mRNA and chromatin-associated RNA modifications and transcription activity with correlation of common genomic features for the larger scientific community.
本网站所有内容来源注明为“梅斯医学”或“MedSci原创”的文字、图片和音视频资料,版权均属于梅斯医学所有。非经授权,任何媒体、网站或个人不得转载,授权转载时须注明来源为“梅斯医学”。其它来源的文章系转载文章,或“梅斯号”自媒体发布的文章,仅系出于传递更多信息之目的,本站仅负责审核内容合规,其内容不代表本站立场,本站不负责内容的准确性和版权。如果存在侵权、或不希望被转载的媒体或个人可与我们联系,我们将立即进行删除处理。
在此留言
















#肥胖# #筛查#
104